ColRobot

Programme: H2020
Topic: ICT-24-2015 Robotics
Project Coordinator: ENSAM – ECOLE NATIONALE SUPERIEURE D’ARTS ET METIERS (FRA)
Start year: 2016 EU Website: https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/688807
Project website: https://colrobot.eu/
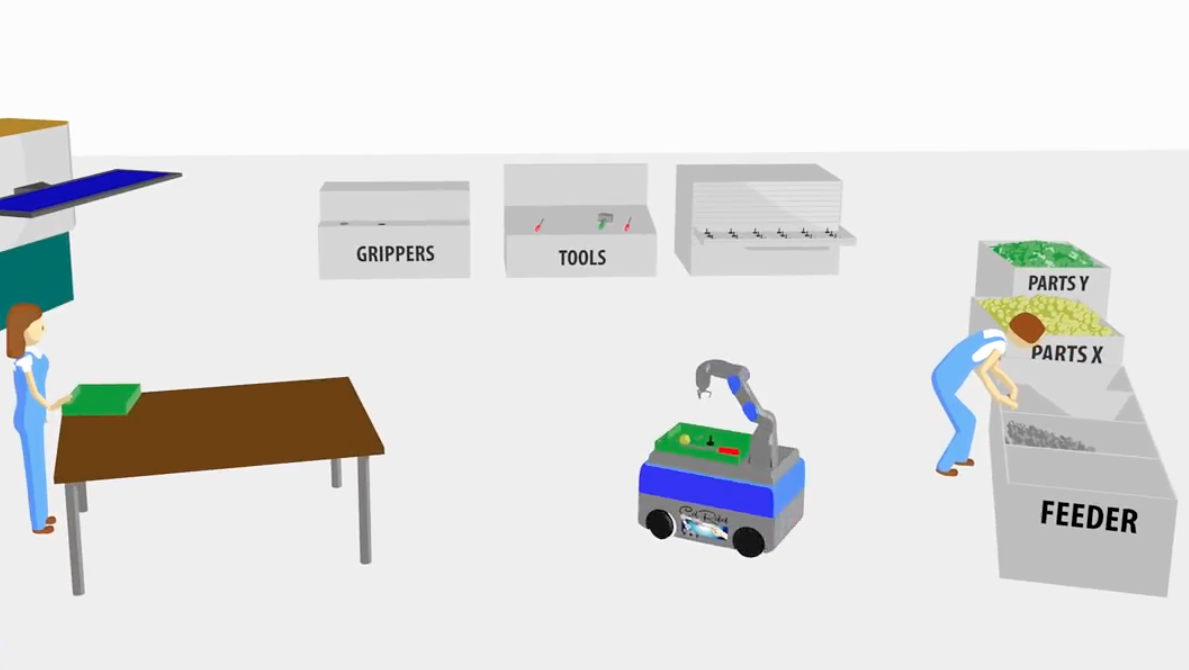
Description
Context
The project moves in the context of manufacturing and robotics production, where competitiveness largelydepends on system productivity, flexibility and agility to react to market demands. Robots are a key element to achieve such competitiveness, especially if they are able to collaborate with humans in a shared workspace in the shop-floor, creating a co-working partnership. The paradigm for robot usage has changed from an idea in which robots work with complete autonomy to a scenario in which robots collaborate with humans. This means taking the best of each partner, human and robot, by exploring the cognitive and dexterity capabilities of humans (focus on value-added tasks) and the capacity of robots to produce repetitive work and provide assistance.
Project
ColRobot combines cutting-edge European robot technology and end-user requirements for assembly processes to create an integrated system for
collaborative robotics in which a mobile manipulator acts as a “third hand” by delivering kits, tools, parts, and holding work pieces while the operator works on it. Humans will cognitively and physically interact with ColRobot robots using gestures, touch commands and demonstrations. The robot will be able to navigate autonomously in the factory floor to pick up the required parts and tools, and prepare kits for assembly. A safety system that pushes the limits of standardization in collaborative robotics supervises the process. The technology readiness level (TRL) will be increased by means of continuous iterative real world testing (performance, usability, relevance in manufacturing), validation and improvement. Two use cases in automobile and aerospace industry will be implemented and validated in real world operational environments. The ColRobot vision and the consortium competences in technology transfer will reduce the technological innovation gap and ease the transition from science to economic and social impact.
XiLAB defines advanced engineering method based on deep learning techniques for intelligent robotic grasps of unknown objects, promoting human-robot collaboration.
Media
Related publications
Bergamini, L., Sposato, M., Pellicciari, M., Peruzzini, M., Calderara, S., & Schmidt, J. (2020). Deep learning-based method for vision-guided robotic grasping of unknown objects. Advanced Engineering Informatics, Vol. 44, 101052.
